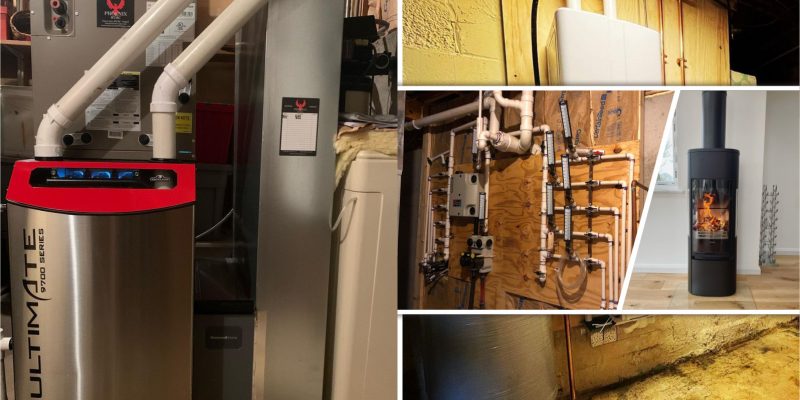
During the cold months, people often rely on home heating systems to stay warm and comfortable. Although there are various types of heating systems available, this article will provide you with some fundamental information to help you understand the basics.
What Are Home Heating System?
Types of Home Heating
There are several types of home heating systems, including:
- Forced Air Systems: These systems use a furnace to heat air, which is then distributed throughout the home via ducts and vents.

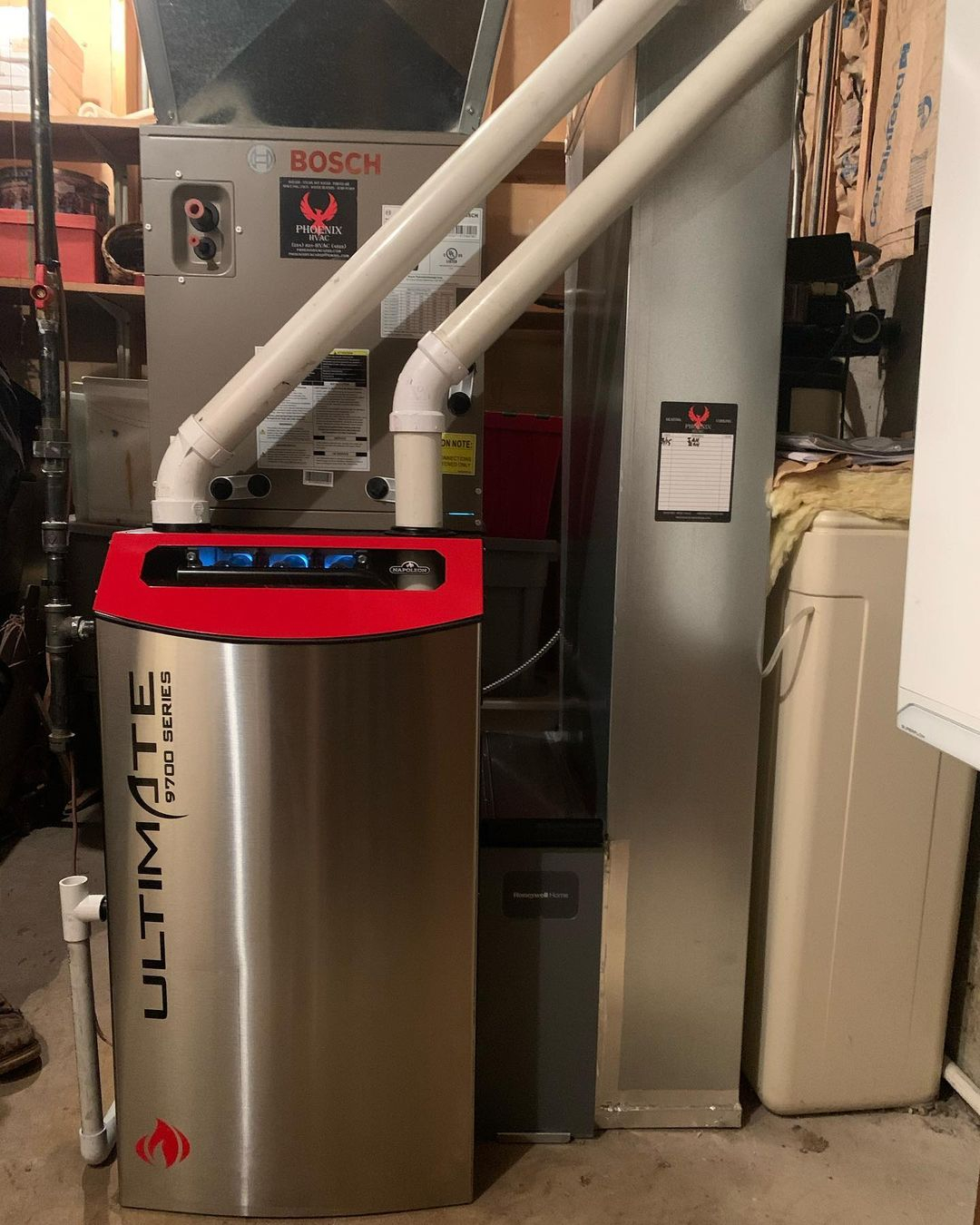
This forced air system has the advantage of heating the room faster. Using this tank system will distribute warm air throughout your home and is beneficial for those with allergies or respiratory problems Forced Air System from @hoffman.heating

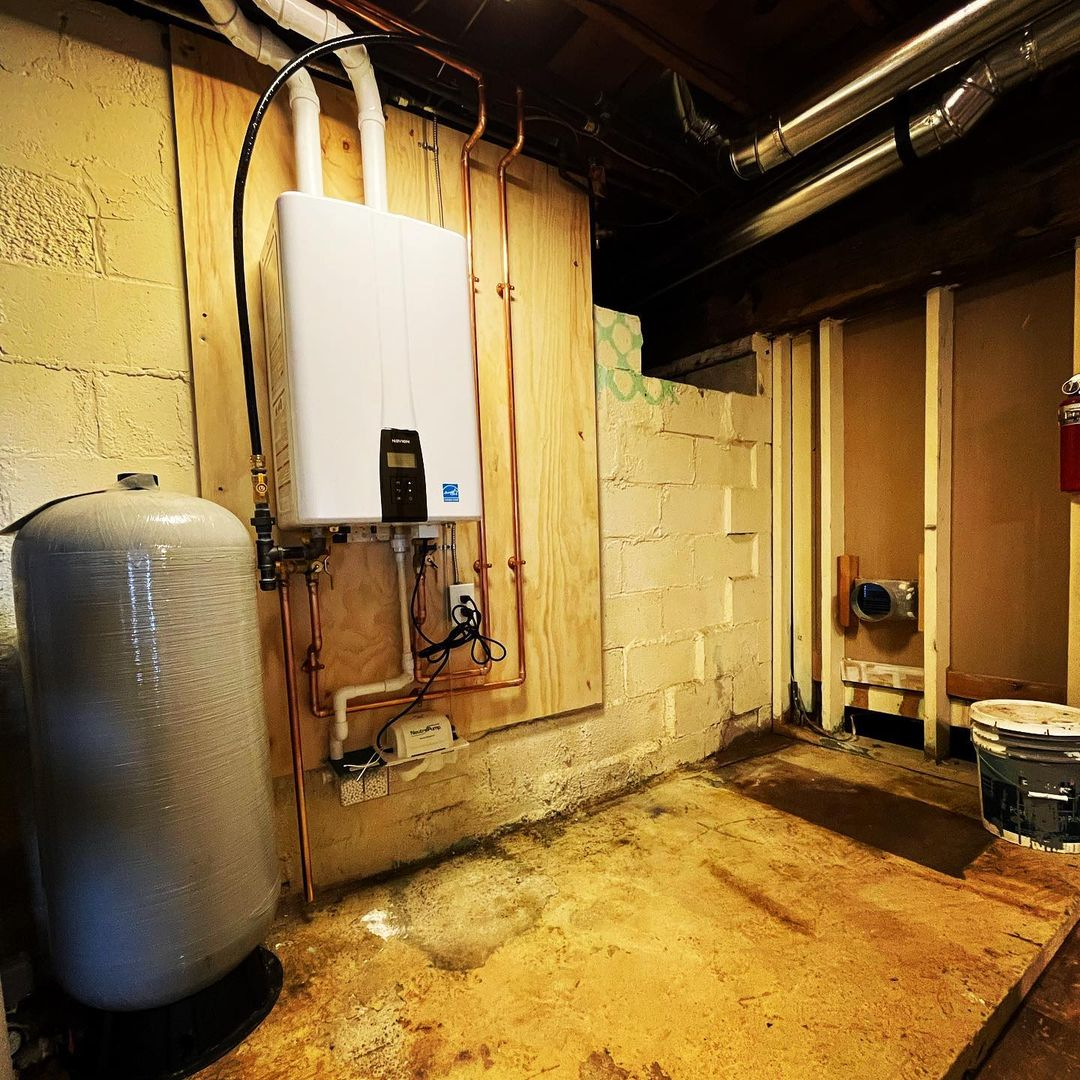
A forced air system using a furnace will supply warm air throughout your home through vents. However, this type of system has the disadvantage that it can circulate allergen dust and other contaminants throughout your home Duel Fuel Forced Air system from @phoenixhvac
- Radiant Heating Systems: Radiant heating systems utilize heated surfaces such as walls, floors, or ceilings to warm up a room.

Radiant heating systems send heat through the floors, walls or ceilings of a building. These systems rely largely on radiant heat transfer and the direct delivery of heat from warm surfaces to occupants and objects via radiation. Radiant Heating Applications from @uponorna

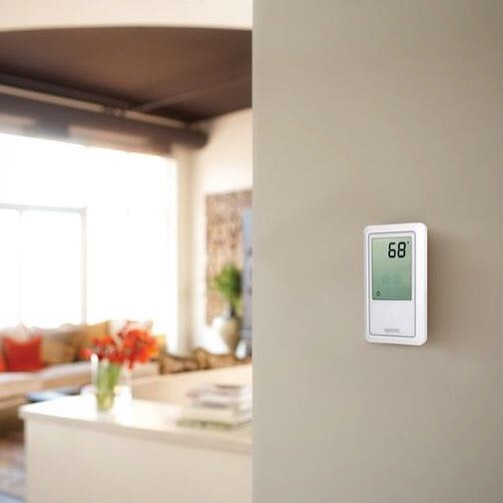
Radiant heating systems supply heat directly to the floor or to panels in the walls or ceiling of the house. Radiant heating is the effect you feel from the warmth of a hot stove element from across a room. You can add this tool to the wall so that it makes it easier for you to use and manage it. Radiant Heating Systems from @futurehometechnology
- Hydronic Heating Systems: These systems circulate hot water or steam through radiators, baseboards, or other types of heating elements to provide warmth.

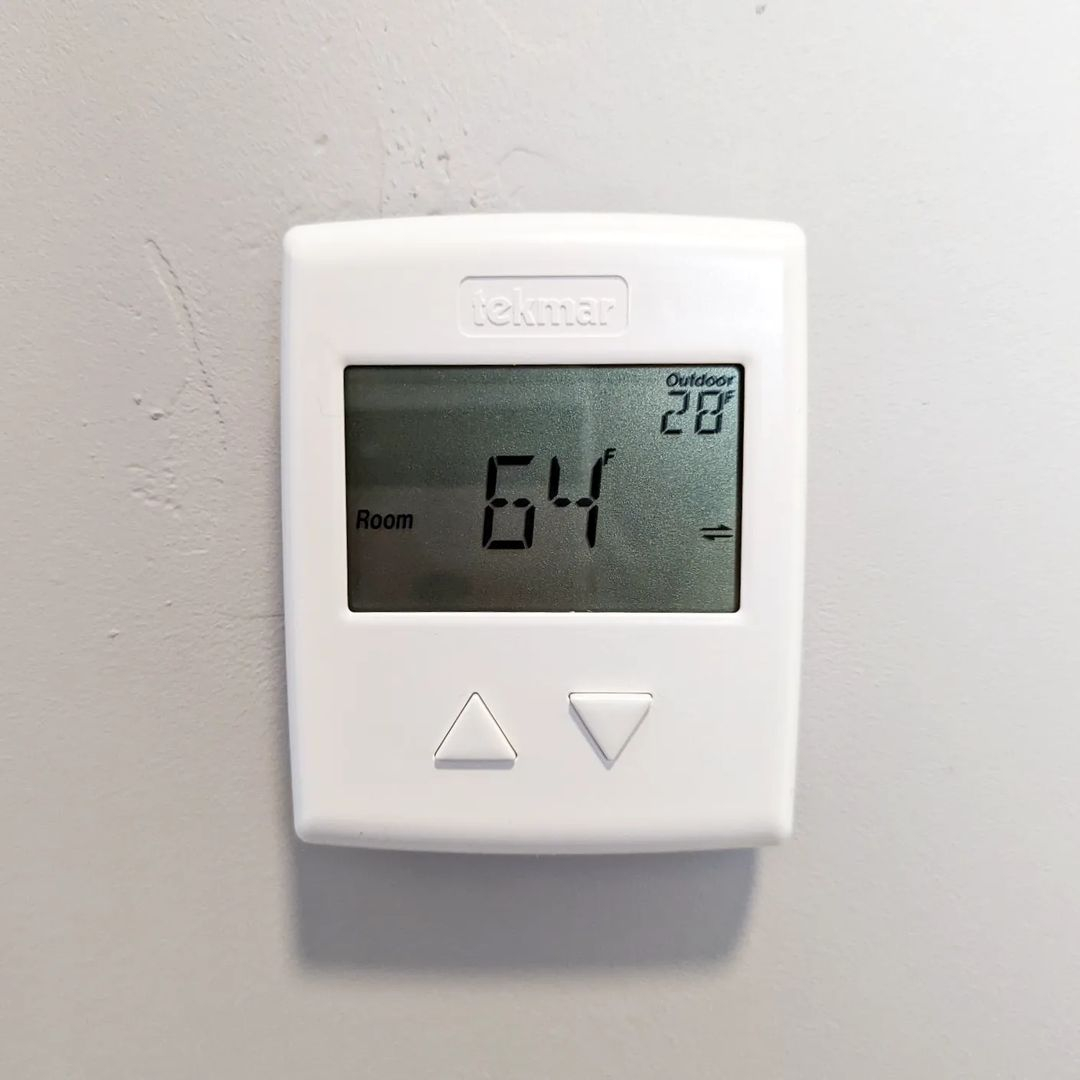
Hydronic heating produces a gentle, hygienic and pleasant form of heat. Many common heating systems circulate airborne contaminants, allergens and dust around homes and buildings. Using this hydronic system will circulate hot water or steam through a radiator. Hydronic Heating System from @camper_reparadise

Modern hydronic heating systems also allow you to control the temperature of each area with a thermostat so that it can be adjusted to suit which room is occupied and individual needs. This minimizes heat loss and energy consumption which means lower environmental impact and electricity bills. Hydronic System from @currentlywandering
- Heat Pump Systems: Heat pumps transfer heat from the outside air or ground into the home, and can also be used for cooling in the summer.
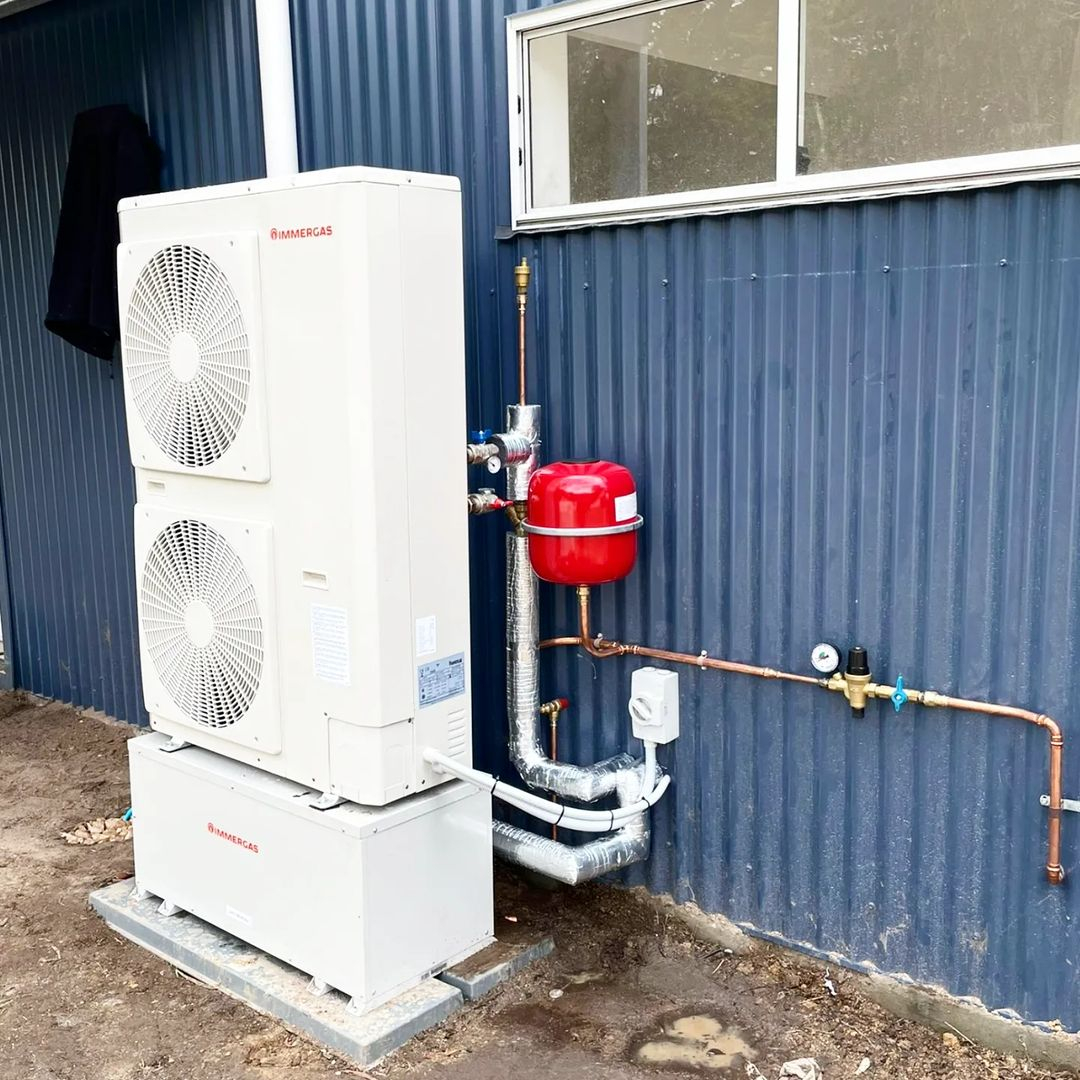

A heat pump is a device that can provide heat to a building by transferring heat energy from outside using the refrigeration cycle. You can put it outdoors so that it will make it easier for you when cooling the building by removing heat from the closed space and throwing it outside. Heat Pump from @melbournehydronic
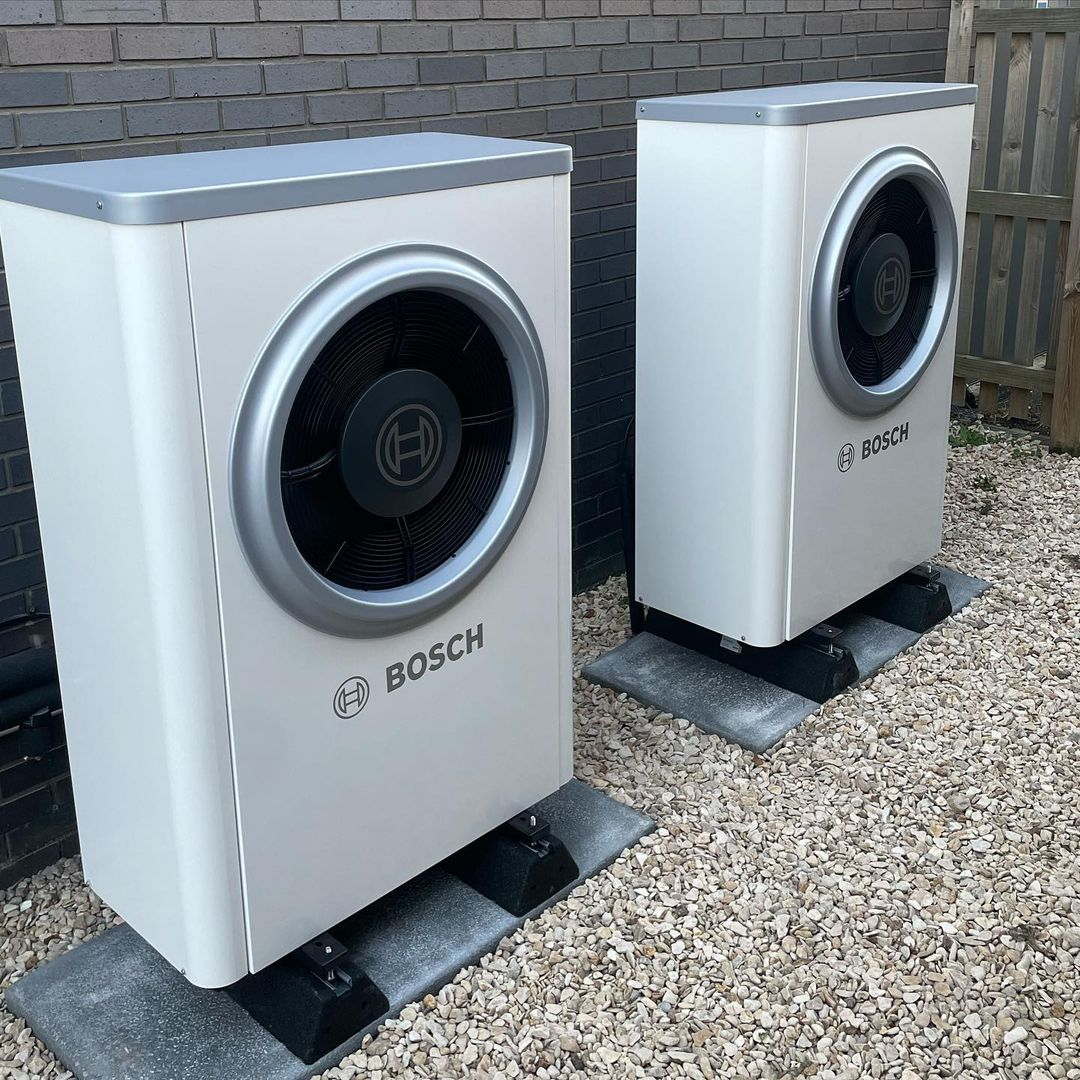

Hybrid heat pump refers to a system that uses a heat pump in addition to another heat source. Typically, this involves installing a heat pump alongside the fossil fuel boiler. Placing it outdoors won’t take up much space either. Hybrid Heat Pump from @b.brill_ltd
- Geothermal Systems: These systems use the stable temperature of the earth to heat or cool the home.
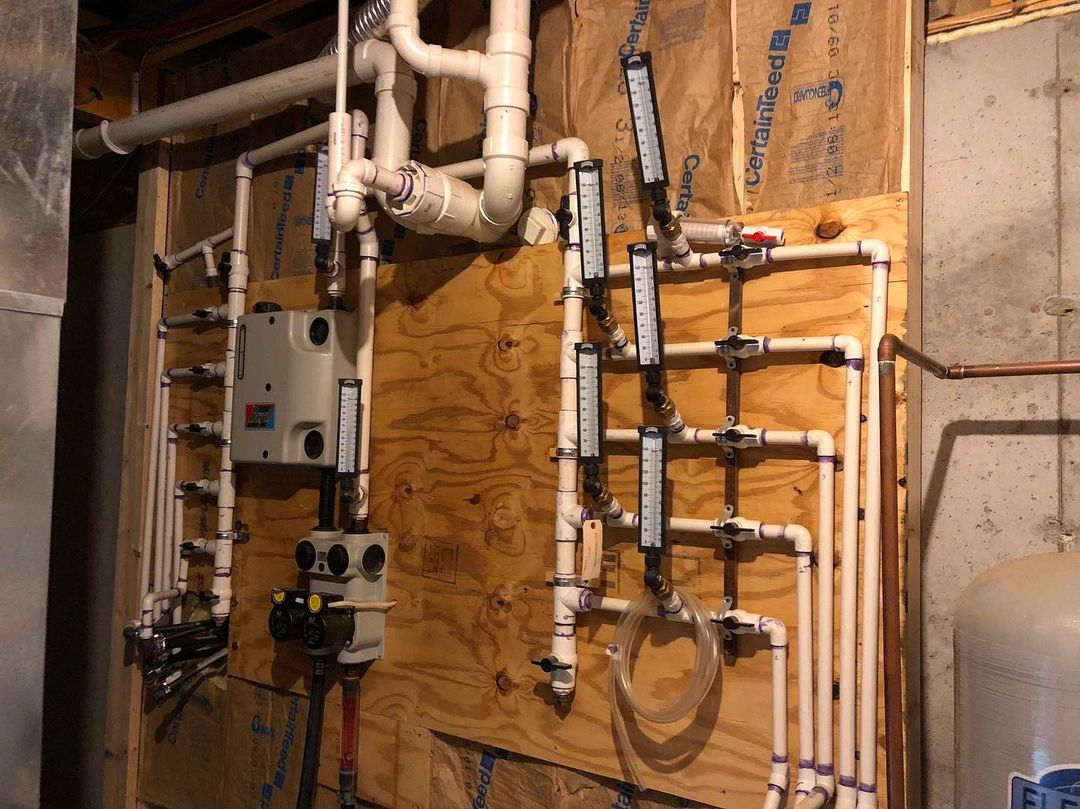

Geothermal heat pump is a heat pump coupled with earth, ground source or water source. They use the relatively constant temperature of the earth as a medium of exchange instead of the outside air temperature. Geothermal Heating System from @abodeteam
- Wood-Burning Stoves: These stoves burn wood to produce heat and can be an efficient and cost-effective heating option.
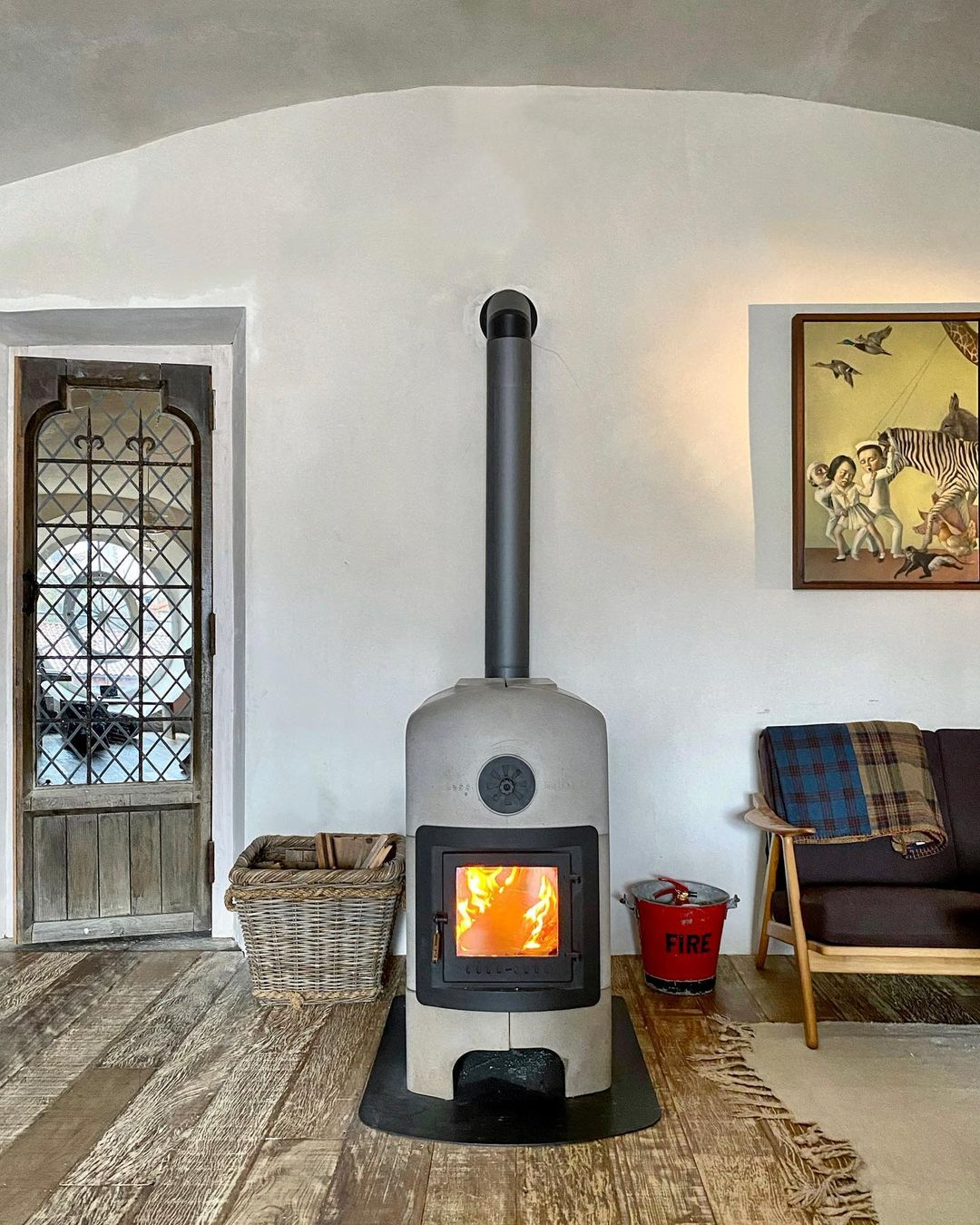

A wood-fired stove is a heating or cooking tool that can burn wood fuel throughout your home. Applying this to the living room gives a warm impression to the whole house and can be an efficient heater for your home. Wood Burning Stove from @eelkejanbles
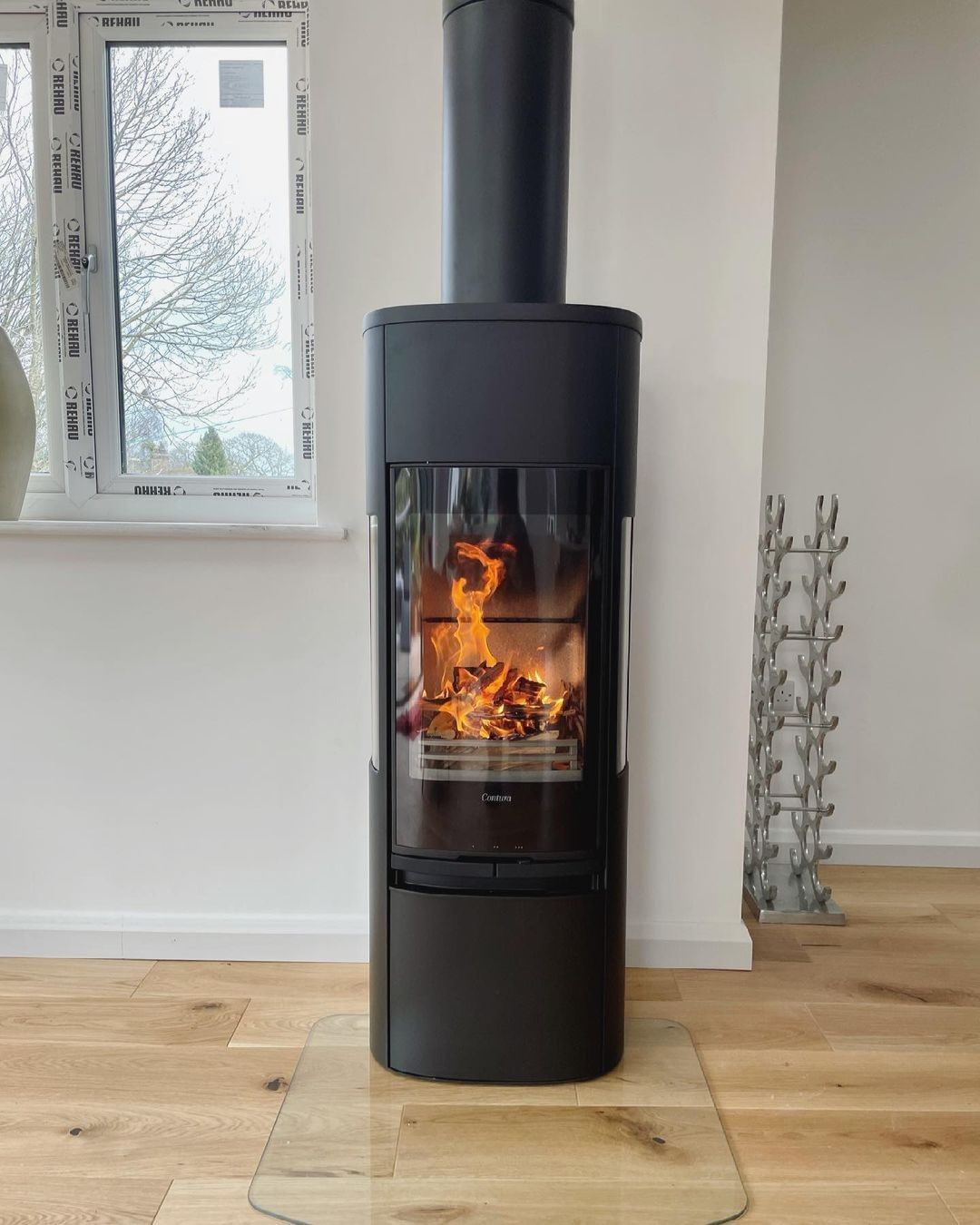

This wood-fired stove will provide extra warmth throughout your home. This stove idea can be an efficient and cost-effective heating option. You can apply it in one of the rooms to make the room warmer at night. Wood Burners from @conturastoves
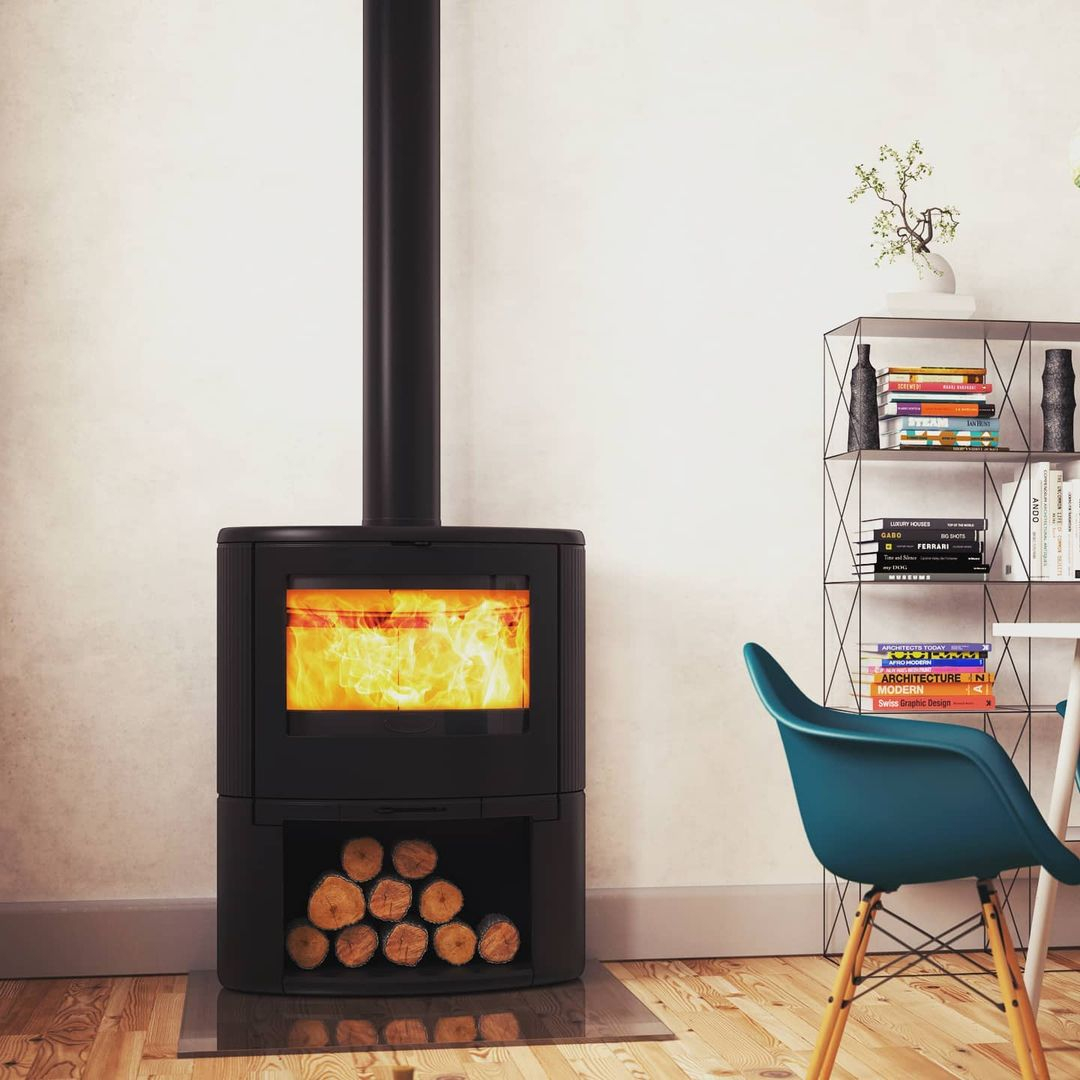

A wood-fired stove is a cost-effective heating option for homes with access to a good supply of firewood. The material selection of this iron will also make this type of heating design last longer and give a minimalist look. Wood Burning Heat from @dovrefire
- Electric Heating Systems: Electric heating systems use electricity to generate heat and can be used for baseboard heaters, radiant floor heating, or other types of electric heaters.

Finally, using this electric heating system uses electricity to make it easier for you to install it. You can put it on the floor of your house to create extra warmth throughout the room. Electric heating systems from @gillgreen_property
Pros And Cons
Forced Air Systems
Pros: Forced air systems have several advantages, including their ability to heat up a room quickly, making them an ideal option for those who want to quickly warm up their homes. Many forced air systems can also be used for air conditioning, providing year-round climate control. These systems can filter the air in your home, which can be beneficial for those with allergies or respiratory issues. Additionally, forced air systems can be divided into different zones, allowing you to heat or cool different areas of your home separately, and they can be cost-effective to install and operate compared to other heating systems.
Cons: These systems can be noisy due to the sound of the air moving through the ductwork, and although they can filter the air, they can also circulate dust, allergens, and other contaminants throughout your home. Forced air systems may not heat a room evenly, with some areas receiving more heat than others, and the ductwork in these systems may need regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent airflow problems and maintain efficiency. Furthermore, ductwork can be a source of energy loss, with heated air escaping through leaks and cracks in the system.
Radiant Heating Systems
Pros: This system provide even heating, eliminating hot and cold spots, and create a more comfortable and natural heat by heating objects in the room, rather than just the air. They are also more energy-efficient than forced air systems, as they don’t rely on ductwork that can lead to heat loss. Radiant heating systems operate quietly, without the sound of air moving through ducts, and require little maintenance once installed. However, they can be more expensive to install, and if repairs are needed, they can be more difficult and costly to access. They also have a slower heating time than forced air systems, which may not be ideal for those who want to quickly warm up their homes.
Cons: One of the main drawbacks is the cost, which can be expensive, especially in existing homes. These systems can also take longer to heat a room compared to forced air systems. Additionally, radiant heating systems can’t be used for air conditioning, so separate cooling systems are required. These systems work best with certain types of flooring, such as tile or wood, and may not be suitable for carpeted areas. There is also a potential for damage if not installed properly, as heavy furniture or flooring installations can damage the system.
Hydronic Heating Systems
Pros: Hydronic heating systems are highly energy efficient, as they use water to transfer heat throughout the home, which is an excellent conductor of heat and can retain heat longer than air. These systems can heat a room evenly and quietly, without the sound of air moving through ducts. Hydronic systems can be divided into different zones, allowing you to heat different areas of your home separately. Moreover, these systems can be used for both heating and cooling by adding a chiller to the system, making them a flexible option for year-round climate control.
Cons: The installation cost of hydronic systems can be high, especially in existing homes, and regular maintenance is required, including water treatment and flushing of the system. There is also a potential for leaks, which can cause damage to your home. These systems may take longer to heat a room compared to forced air systems, and they can’t be used for air conditioning, requiring separate cooling systems.
Heat Pump Systems
Pros: Heat pump systems can be a great option for those looking for an energy-efficient heating and cooling solution. These systems transfer heat rather than generate it, making them more efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems. In addition to providing both heating and cooling for your home, heat pumps have a long lifespan of up to 20 years with proper maintenance. They also operate quietly and have low emissions since they use electricity instead of burning fossil fuels. Overall, heat pump systems offer a versatile and environmentally-friendly option for home heating and cooling.
Cons: The higher upfront cost, limited effectiveness in extreme temperatures, potential for refrigerant leaks, regular maintenance requirements, and increased electrical demand.
Geothermal Systems
Pros: Geothermal systems offer several pros, including energy efficiency, dual function, long lifespan, low emissions, and low operating costs. These systems transfer heat from the ground and can provide both heating and cooling for your home. They have a low environmental impact, and operating costs can be lower compared to traditional heating and cooling systems.
Cons: Geothermal systems also have some cons. They can be more expensive to install, may not be suitable for all locations, require specialized knowledge and expertise for installation, and have a potential for ground loop damage. Additionally, these systems require regular maintenance, including checking the loop fluid, to ensure proper operation and energy efficiency.
Wood-Burning Stoves
Pros: Wood-burning stoves are a cost-effective heating option for homes with access to a supply of firewood, providing a high heat output and reliable backup heat source during power outages.
Cons: They also pose pollution and safety hazards if not used properly, and require regular maintenance and cleaning to prevent the risk of chimney fires. Additionally, wood-burning stoves offer limited temperature control compared to other heating systems, which may require more frequent adjustments.
Electric Heating Systems
Pros: Electric heating systems offer several pros, including easy installation and low upfront costs, no emissions, and quiet operation.
Cons: High operating costs, limited effectiveness in extreme temperatures, dependency on electricity, and lower efficiency compared to other heating systems. It’s essential to consider the pros and cons of electric heating systems when deciding which heating option is best for your home.Comparing Home Heating Systems: Which is Best for You?